Maximize Claude Code: 16 Practical Tips (Advanced Techniques, Worth Bookmarking!)
Original Source: WeChat Public Account "AI Tech Geek"
Original Author: R哥
Published: July 8, 2025, 10:31
Hello everyone, I'm R哥.
In recent years, AI programming tools have become increasingly popular, especially terminal-level AI programming assistants like Cursor and Claude Code. When used properly, they can significantly boost programmer productivity.
However, many developers get stuck on "not knowing how to ask questions," "not knowing how to break down requirements," and "not knowing how to control context." They only know how to ask simple questions and miss out on many practical techniques, resulting in code that doesn't meet their expectations.
Today, I'll guide you through how to efficiently use Claude Code for development and productivity enhancement, eliminating inefficient manual work! (This content is packed with value - recommend bookmarking for later reference~)
For Claude Code installation and usage, first read this:
1. Be Specific with Your Requirements
Stop saying generic commands like "Fix this bug". Try to be specific with your requirements.
You can say it like this:
Fix the null pointer error that occurs when users login without entering a password
2. Break Complex Requirements into Steps
For small tasks/modules, you can send requirements to AI all at once for a complete result, which is more efficient overall.
However, for large requirements with long implementation processes, it's recommended to break complex tasks into small steps, such as:
- Create a new API interface for users
- Add necessary validation for request fields
- Write test cases for this interface
- ...
Because AI context has limitations, overly long context/memory might result in incomplete output or even truncation. Breaking it down step by step is safest - you can review/test each step before letting AI execute the next one.
Like the example above, it's actually not that complex and can be sent to Claude Code all at once. AI can consider code structure and style holistically, reducing repetitive explanations and communication costs.
3. Understand Project Code Before Starting
Before modifying code, let Claude understand your code first, such as:
- Analyze the database table structure
- How are errors handled in this application?
- ...
Before making changes, let AI understand your business and code so it can assist you more precisely and efficiently in development and optimization.
4. Learn to Use Shortcuts to Save Time
For example:
- Type
/to see all slash commands - Use up/down arrow keys to view command history
- Use Tab key for quick command completion
- Use Option + Enter to create new lines
- Use Ctrl + C to exit terminal, etc.
5. Use Permission-Free Mode
Do you often encounter Claude Code stopping mid-task to ask for authorization?
Without authorization, it gets stuck there. Although you can set "don't ask again" in the current session, there are several types of permissions, and each type needs to be asked, severely affecting efficiency.
Actually, there's a parameter when starting Claude:
claude --dangerously-skip-permissionsWhen starting with this parameter, Claude Code will show a warning:
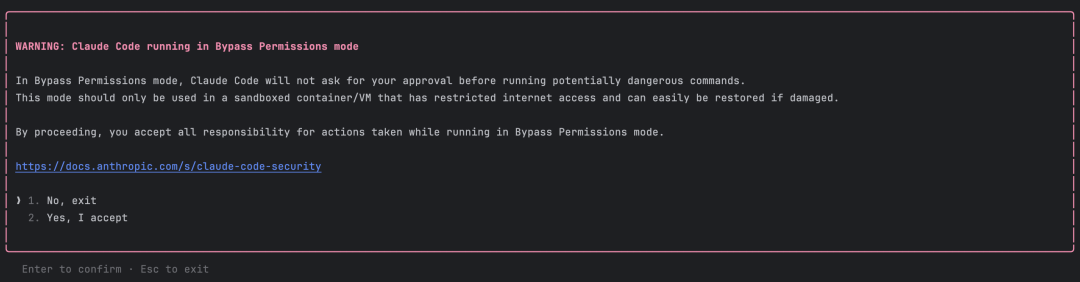
You need to click confirm (Yes) to enable Bypassing Permissions mode. After enabling this mode, a yellow Bypassing Permissions mode prompt will appear at the bottom of the terminal:
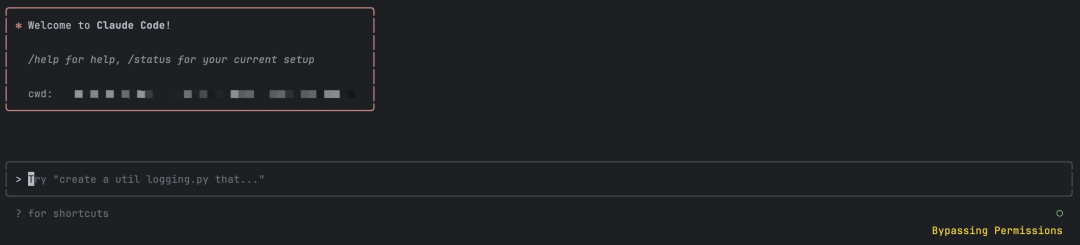
After enabling Bypassing Permissions mode, all subsequent operations won't require your authorization - Claude Code will complete all tasks directly.
Typing claude --dangerously-skip-permissions every time is too cumbersome and error-prone. You can consider creating an alias:
alias claude='claude --dangerously-skip-permissions'
This only takes effect temporarily. For permanent effect, add it to your personal environment configuration file and source it.
6. Activate Deep Thinking Mode
In Claude Code, you can use the word "think" to activate deep thinking mode, including the following levels:
"think" < "think hard" < "think harder" < "ultrathink"
Using these deep thinking modes directly corresponds to different levels of thinking budget in the system. Each level progressively increases Claude's available thinking budget. Undoubtedly, using ultrathink is the most expensive but can unleash its maximum potential.
If you're subscribed to the Max plan, consider using ultrathink mode; otherwise, be careful with your wallet.
For example, let me test:
1+1=? ultrathink
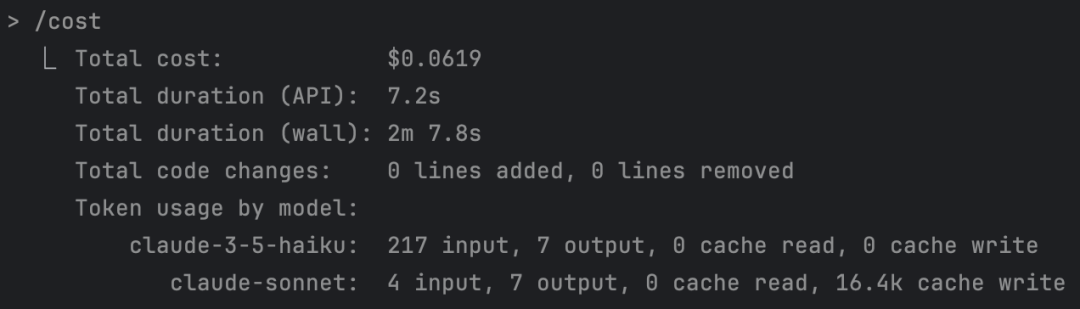
A simple 1+1 calculation cost $0.06, about 5 cents RMB...
7. Interrupt Work When Commands Are Wrong
If Claude Code is working and you gave the wrong command description, if you want it to stop, just press the ESC key:

The terminal will show "interrupted by user."
8. Send Images for Processing
Claude Code can send images and process them. In the command line, send images with prompts to help it better understand your intentions.
As shown:
Note: On Mac, pasting images is not done with command + v, but with ctrl + v shortcut.
You can also send the following commands:
- What does this image show?
- This is an error screenshot - what caused it?
- Please design a webpage based on this design mockup
9. Resume Historical Sessions
Non-Interactive Mode
Claude Code provides two options to resume previous conversations:
claude --continueorclaude -c: Automatically continue the most recent conversation without any promptsclaude --resumeorclaude -r: Show historical conversation selector
These parameterized commands need to be executed in "non-interactive mode" - that is, before entering Claude Code.
Interactive Mode
If you've already entered a Claude Code session and want to resume a previous historical session, you can use the /resume command:

Use up/down arrow keys to select a record to resume the session.
10. Memory Management
Memory File Introduction
Claude Code provides three memory locations, each serving different purposes:
| Memory Type | File Location | Purpose | Usage Example |
|---|---|---|---|
| Project Memory (Shared) | ./CLAUDE.md | Team-shared project instructions | Project architecture, coding standards, common workflows |
| User Memory (Global) | ~/.claude/CLAUDE.md | Personal preferences for all projects | Code style preferences, personal tool shortcuts |
| Project Memory (Local) | ./CLAUDE.local.md | Project personal preferences (deprecated) | Your sandbox addresses, test data preferences, etc. |
The CLAUDE.md file is a memory file automatically read by Claude Code, similar to the rules file in Cursor, but more powerful. It can provide more project-related context information to Claude, such as:
- Common bash commands
- Core files and utility functions
- Code style guides
- Testing instructions
- Codebase standards
- Development environment setup
- More information you want Claude to remember
When Claude Code starts, all the above memory files are automatically loaded into the runtime environment.
You can place CLAUDE.md files in multiple locations. Claude Code will recursively read these files, starting from the current working directory and recursively going up to the root directory, reading any CLAUDE.md files found.
Editing Memory Files
During a session, use the /memory slash command to open memory files in the system editor:
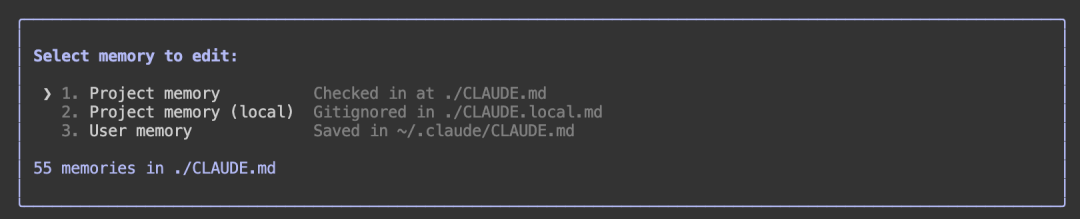
Select a memory file and press Enter to edit. The first one is generated using the /init initialization command, the second is deprecated, and the third is the user-level memory file.
For example, we can modify the third user-level memory file:
Please answer me in Chinese every time.
After setting this memory, all subsequent project interactions will be in Chinese.
11. Interact with Git
In Claude Code, our Git operations can become conversational, without needing to remember cumbersome commands.
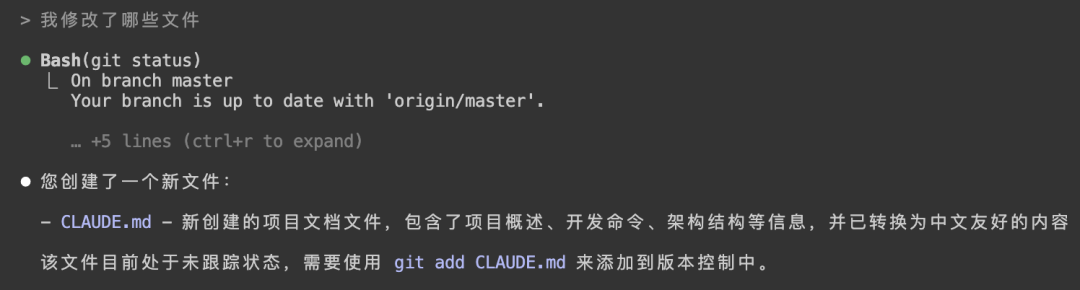
What files have I modified?
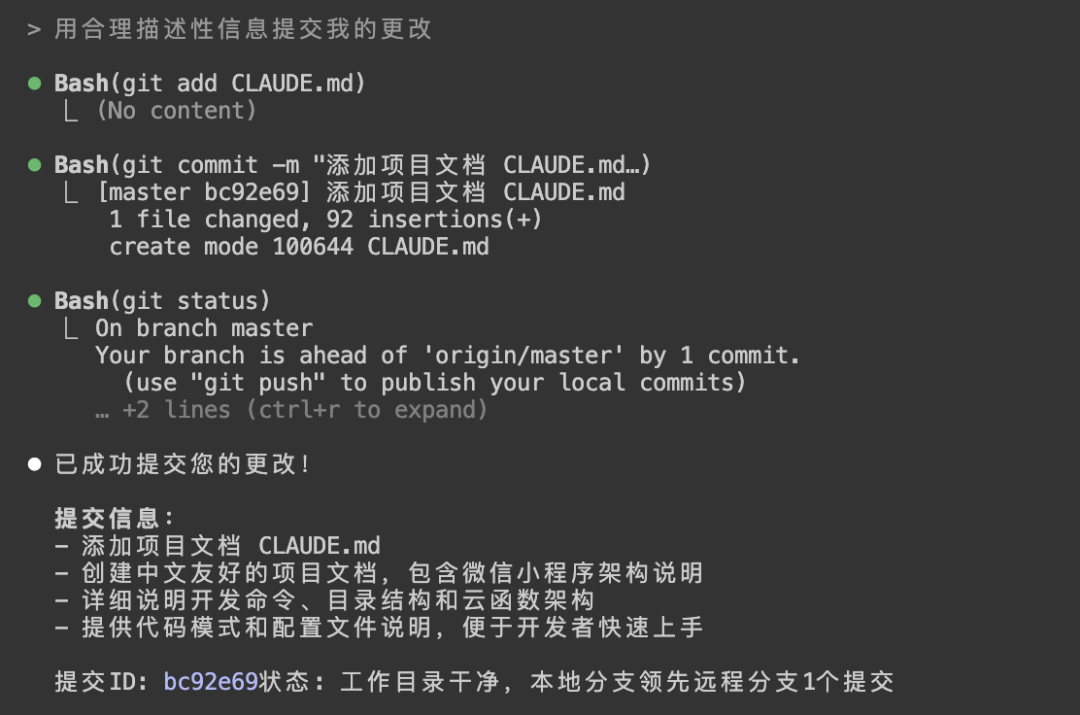
Commit my changes with reasonable descriptive information
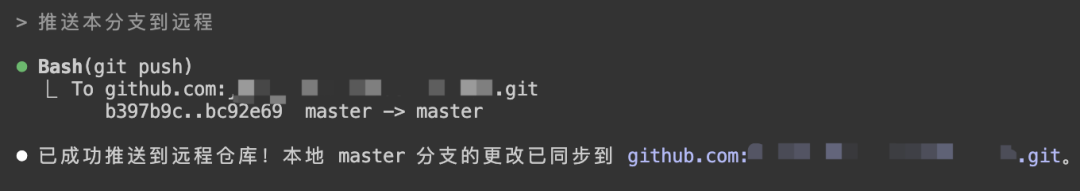
Push this branch to remote
Create a new branch: feature/test
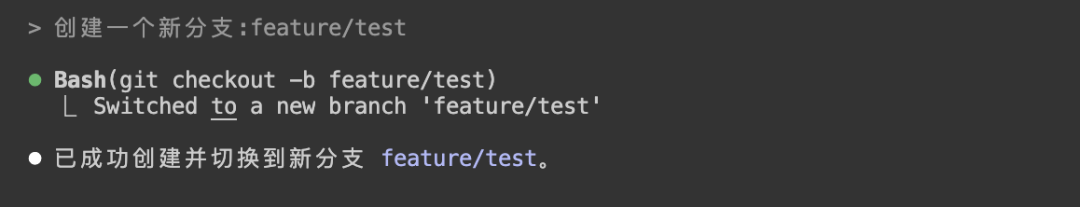
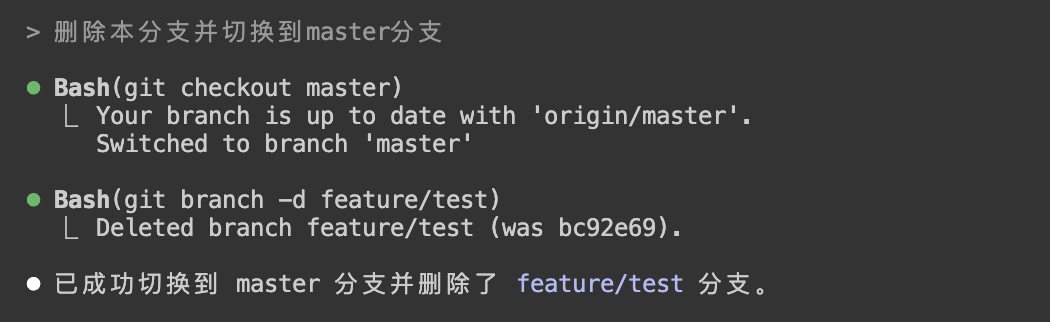
Delete this branch and switch to master branch
Show all file lists from the last 3 commits

Very convenient and quick! Use natural language to interact with Git!
12. Interact with Linux
Since Claude Code is used in terminal form, we can also use it as a Linux intelligent assistant without needing to remember complex Linux commands.
In interactive mode:
List the top 3 .java files with the most lines
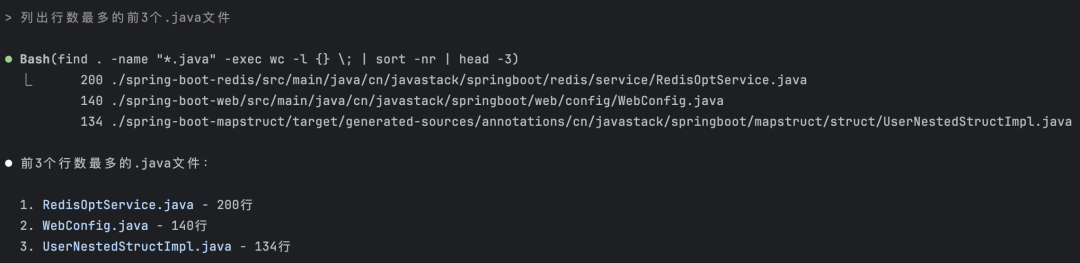
From the execution information, you can see the commands it's executing - such complex commands are generally hard for people to remember.
In non-interactive mode:
claude -p "List the top 3 .java files with the most lines"
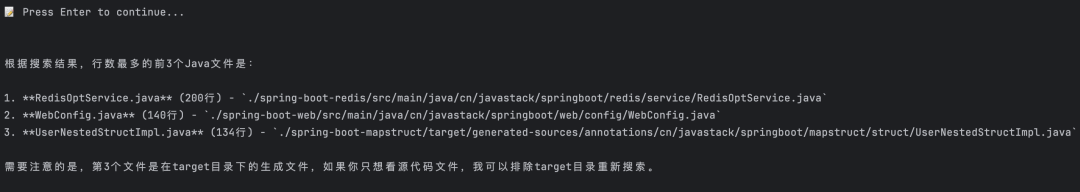
This executes a one-time command. It will list files meeting the criteria and then exit Claude Code interactive mode.
13. Model Switching
Claude Code currently supports flexible switching between Claude Opus and Claude Sonnet 4 models. Use the /model command to switch:
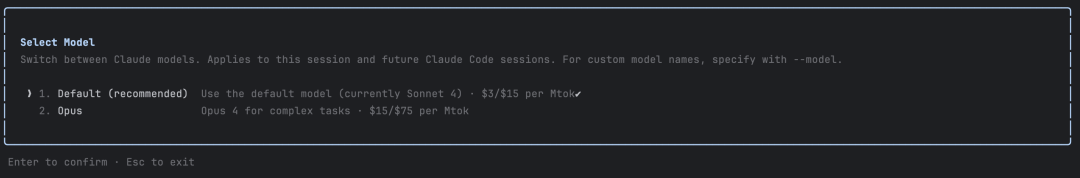
Default is Claude Sonnet 4. You can switch to Claude Opus, but personally I don't think it's necessary. Strongly recommend using Claude Sonnet 4 - its user experience isn't significantly different from Claude Opus, but its billing rate is only 1/5, ignore this if you're wealthy.
Note: Only Max users support Claude Opus and switching. Pro users only support Claude Sonnet 4.
14. Check Usage
Use the /cost command to view current session usage:
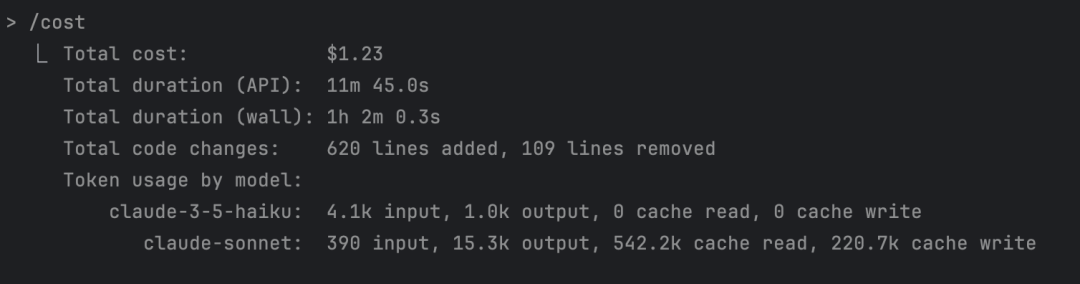
As shown, it displays that my current session has consumed $1.23.
Official usage viewing is too general and not intuitive enough. Recommend using the ccusage tool for viewing.
Install ccusage:
sudo npm install -g ccusage
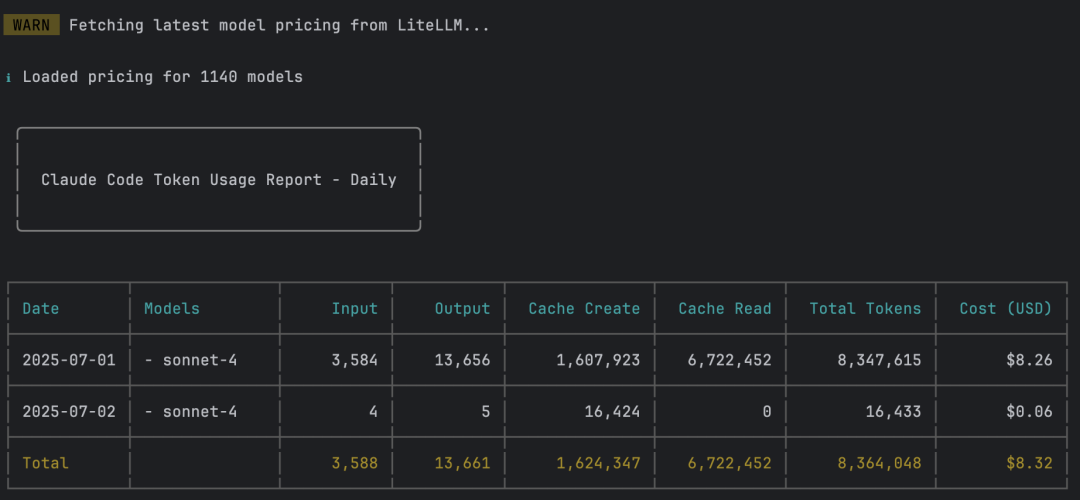
To view consumption since a specific date:
ccusage -s 20250701
To view consumption in real-time:
ccusage blocks --live
Claude Pro/Max subscription users don't need to worry about consumption - it's billed monthly, not by usage amount, as shown below:
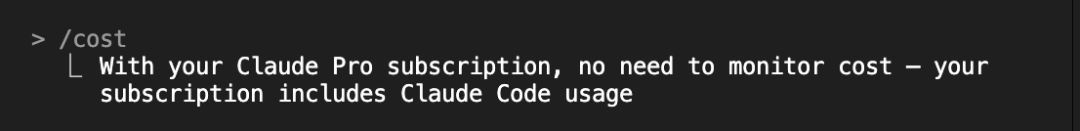
Once you exceed the usage limit, it becomes unavailable:
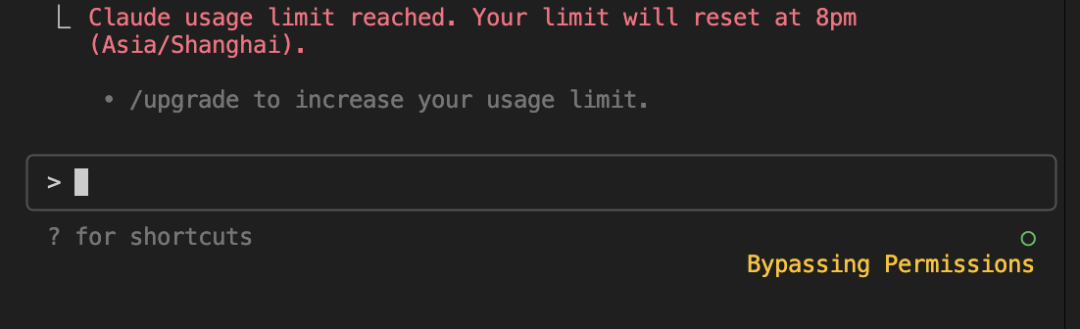
You need to wait until the specified time for recovery.
15. Context Compression
Claude Code provides a /compact compression command:
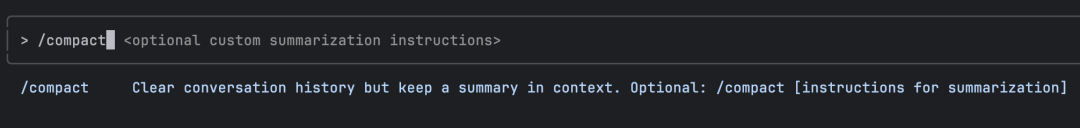
It clears conversation history but retains summaries in context.
The benefits of doing this are:
- Reduce conversation context size: When conversation history becomes very long, using
/compactcan compress conversation content and reduce token usage - Manual compression control: Although Claude Code automatically compresses when context exceeds 95% capacity (can be enabled/disabled via
/config), you can manually trigger compression using/compact
As shown:

When remaining context space is low, the bottom right will show the remaining percentage for automatic compression. When it reaches 0%, compression will occur.
So, to effectively manage cost and performance:
- Recommend regularly using
/compactfor manual compression when context becomes large - Regularly use the
clearcommand to reset context - Break down complex tasks or make requirements as specific as possible
Of course, wealthy users, please ignore this.
16. Custom Shortcut Commands
Usage Introduction
Claude Code supports custom commands. You can create commands to quickly execute specific prompts or tasks, such as:
- Analyze this project's performance and suggest three specific optimization recommendations
- Commit all changed files with reasonable descriptive information, then push to remote repository
- ...
This way, common operations don't require writing lots of text - use custom commands instead.
Custom command syntax:
/<prefix>:<command-name> [arguments]Custom Command Explanation:
- Commands are divided into user-level and project-level
- User-level commands can be used in all projects; project-level commands can only be used in the current project
- User-level commands are placed in the personal
~/.claude/commandsdirectory, while project-level commands are placed in the current project's.claude/commandsdirectory - When using commands, user-level commands use
/user:prefix, project-level commands use/project:prefix, followed by the command file name, can be cascaded - Command files support using
$ARGUMENTSparameter placeholders. When adding parameters after commands like/project:test 123, it will replace$ARGUMENTSmarkers in the command file with123
For example, if there's a .claude/commands/frontend/component.md custom command, the usage method would be: /project:frontend:component.
Practical Application
Project-Level Commands
Create custom command directory in current project:
mkdir -p .claude/commands
Create a project-level optimization command:
echo "Analyze this project's performance and suggest three specific optimization recommendations." > .claude/commands/optimize.md
Use custom command in Claude Code:
/project:optimize
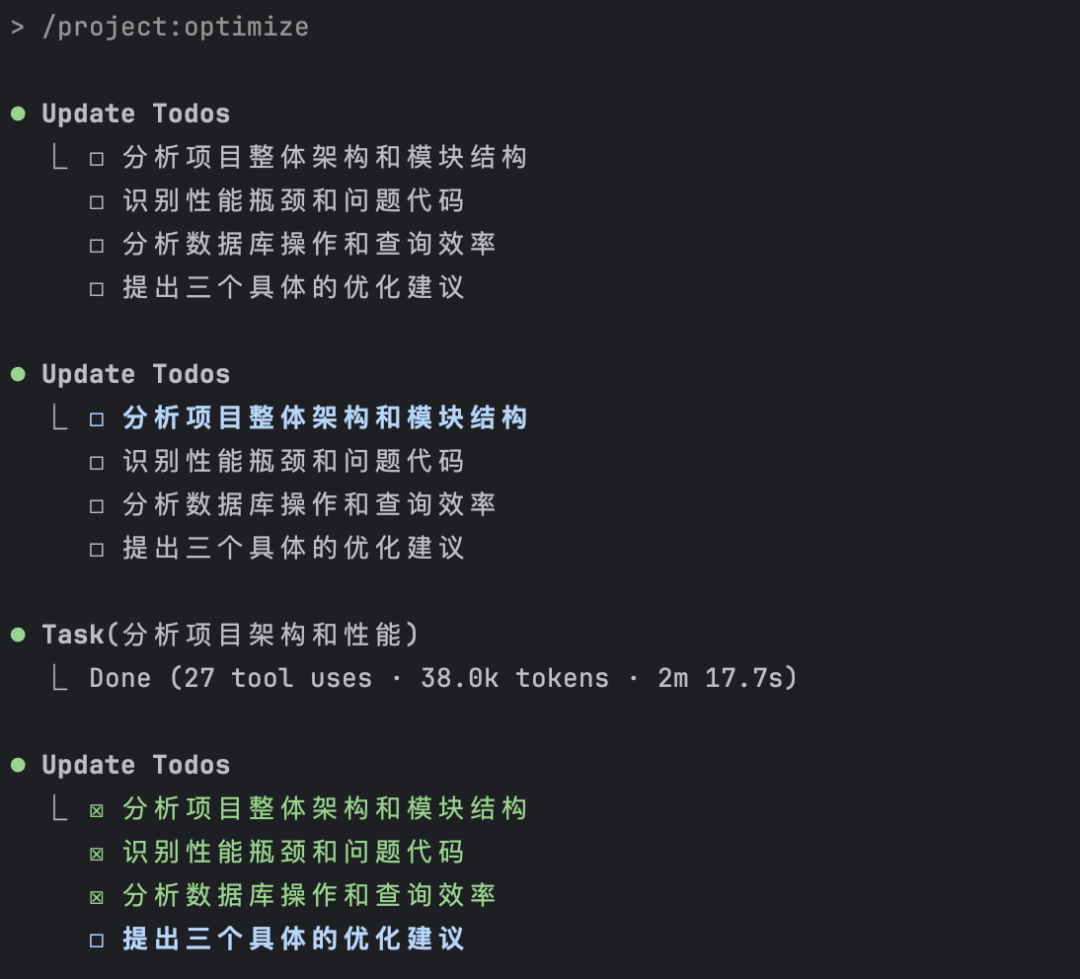
Surprisingly, it even broke down the task itself, analyzing overall project architecture, performance bottlenecks, database operations, then providing optimization recommendations.
User-Level Commands
Create custom command directory in personal directory:
mkdir -p ~/.claude/commands
Create a user-level push command:
echo "Commit all changed files with reasonable descriptive information, then push to remote repository." > ~/.claude/commands/push.md
Use custom command in Claude Code:
/user:push
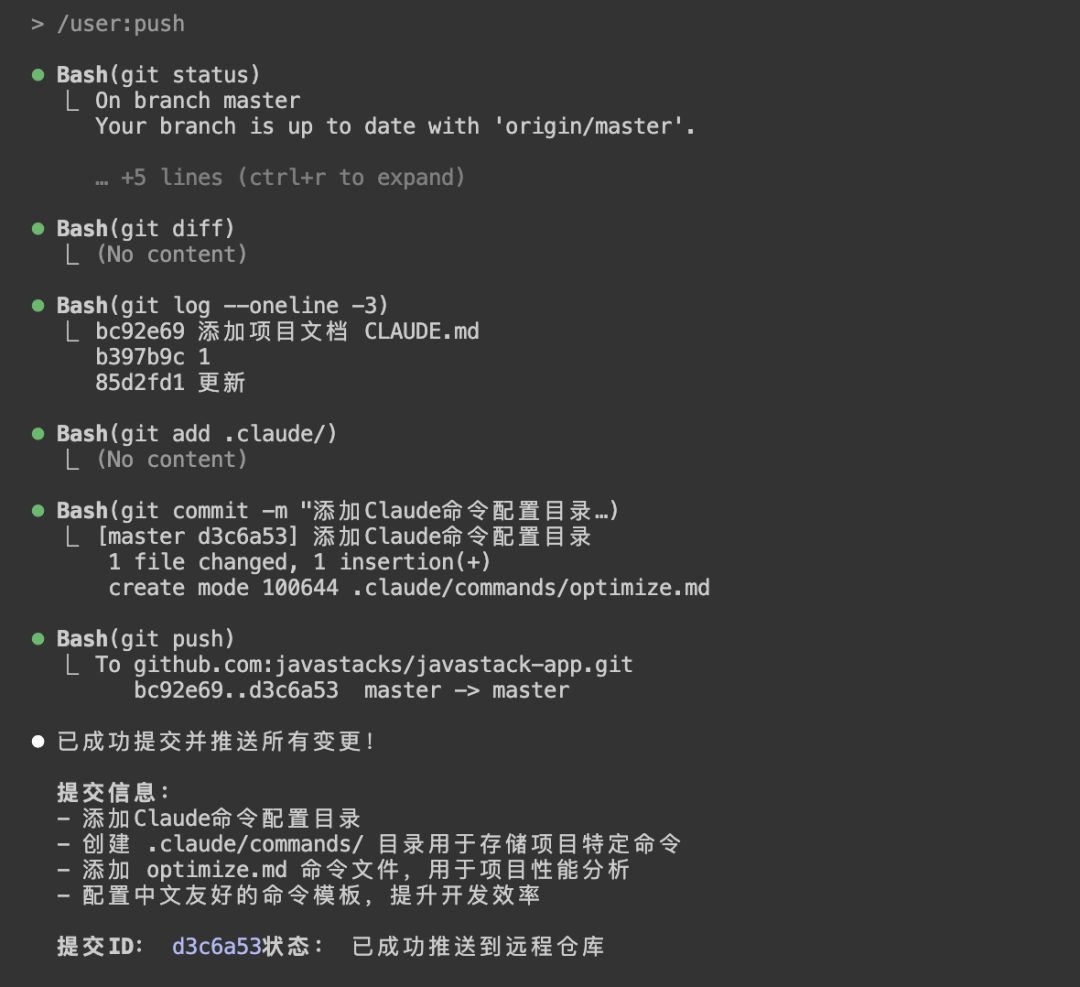
Nice~ This makes Git interaction even simpler!
Well, that's it for this sharing session~
These are my efficient techniques and pitfall-avoidance insights from actual Claude Code programming practice - truly unreserved practical summaries.
AI won't eliminate programmers, but those who can't use AI will be eliminated. Only programmers who can use AI have a future!
To be continued - I'll continue sharing Claude Code insights, experiences, and advanced usage techniques. The public account will continue sharing AI practical content. Follow "AI Tech Geek" public account and learn AI with me.
Copyright Notice: This article is original content from the "AI Tech Geek" public account. Please cite the source when reprinting or quoting this article. Plagiarism and content washing will be reported for infringement, with consequences at your own risk, and we reserve the right to pursue legal responsibilities.
< END >
Recommended Reading:
After using Claude Code, I realized Cursor is weak.
Annual Blockbuster! Global Collection of Hottest AI Programming Tools
What is MCP? How to use it? Explained clearly in one article!
Developing an MCP Server from scratch! Complete tutorial!
62 DeepSeek Universal Prompts (Worth Bookmarking)
33k+ star! All Selected MCP Resources in One Place!
More ↓↓↓ Follow the public account ✔ Star⭐ please
